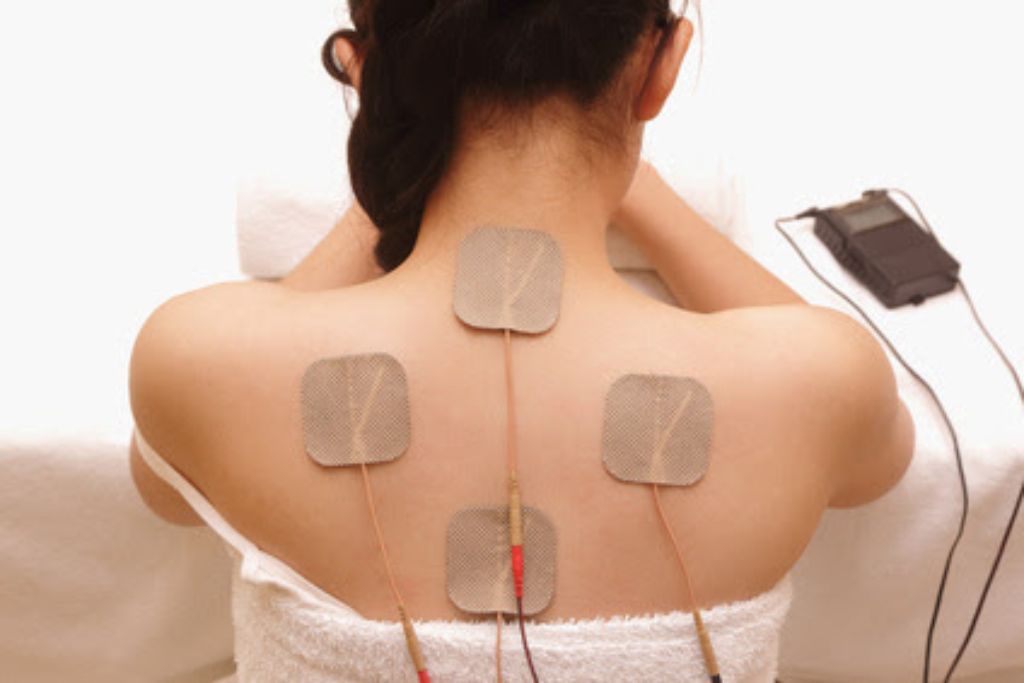
TENS
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation, or TENS, is a non-invasive, drug-free method for managing pain. It works by sending low-voltage electrical impulses to specific areas of the body via electrodes placed on the skin. These impulses help block pain signals from reaching the brain, providing relief to those suffering from a variety of painful conditions.
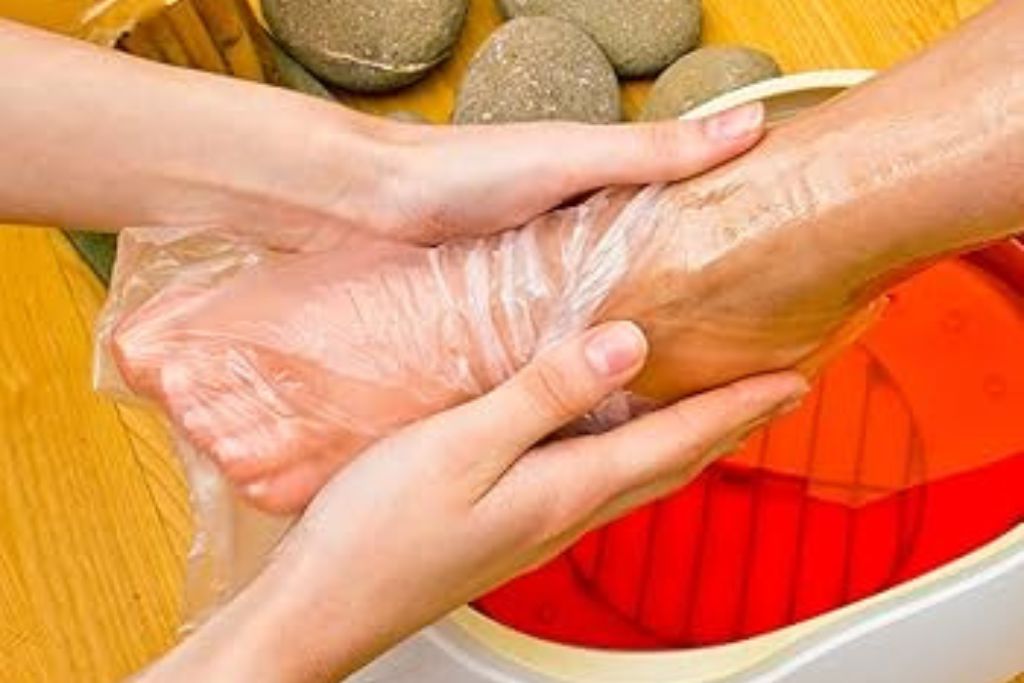

Wax Therapy
Wax therapy is a type of thermotherapy that uses heated paraffin wax to provide heat to the body, usually applied to hands, feet, or other joints. The therapy is commonly used in physical therapy, rehabilitation, and beauty treatments to relax muscles, improve blood circulation, and alleviate pain.
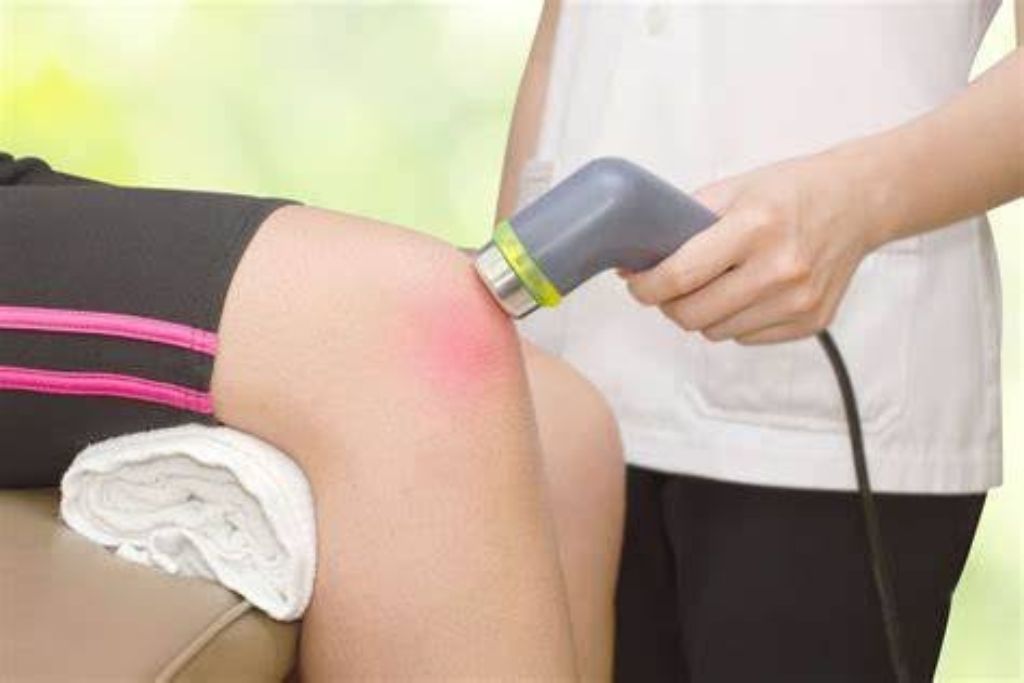
Ultra sonic
Ultrasonic eye therapy is a cutting-edge medical procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to diagnose and treat various eye conditions. With modern technology advancing rapidly, the use of ultrasound in eye care is growing, offering non-invasive and effective treatment options for patients who seek to improve their eye health.
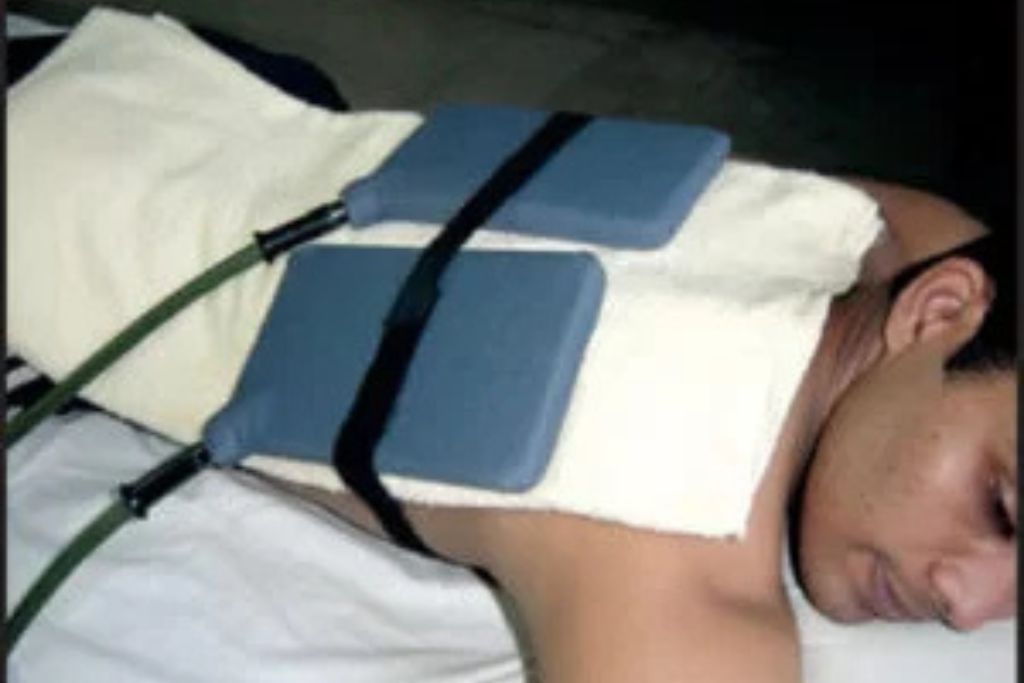
SWD
SWD (Short Wave Diathermy) eye therapy is a treatment that uses electromagnetic waves to promote healing and relieve pain. It's often used for conditions affecting the eye, such as inflammation or dry eye syndrome. The therapy works by increasing blood flow and tissue temperature, which can enhance healing processes.
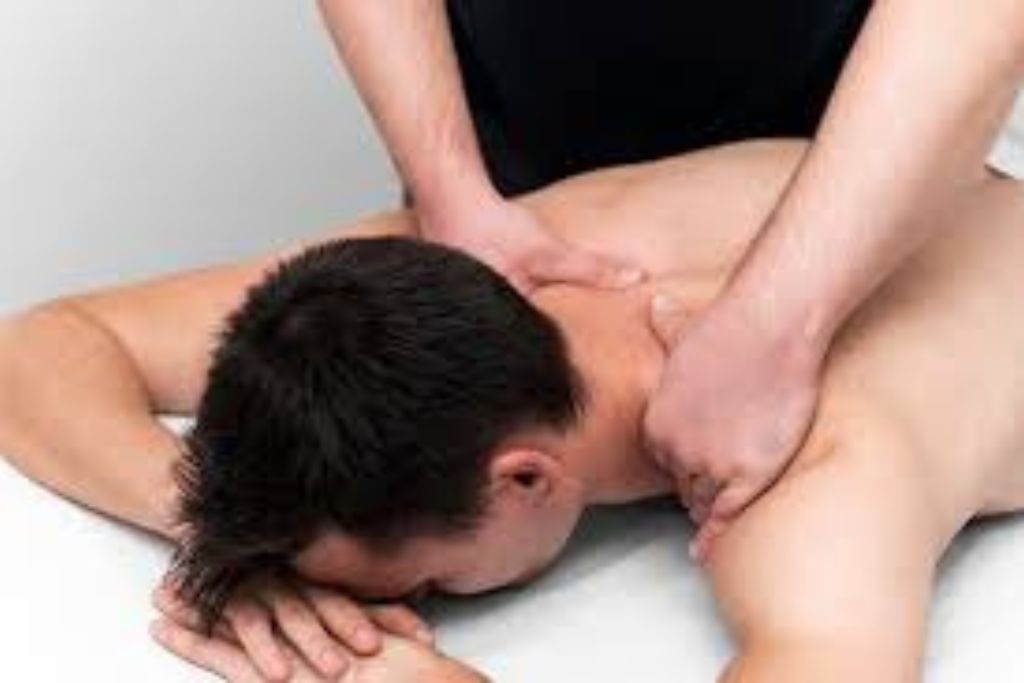
Manual Therapy
Manual eye therapy, often referred to as vision therapy, is a non-invasive treatment aimed at improving various visual functions through exercises and techniques. It is commonly used to address issues like eye strain, poor focus, and visual coordination problems such as strabismus (eye misalignment) or amblyopia (lazy eye).
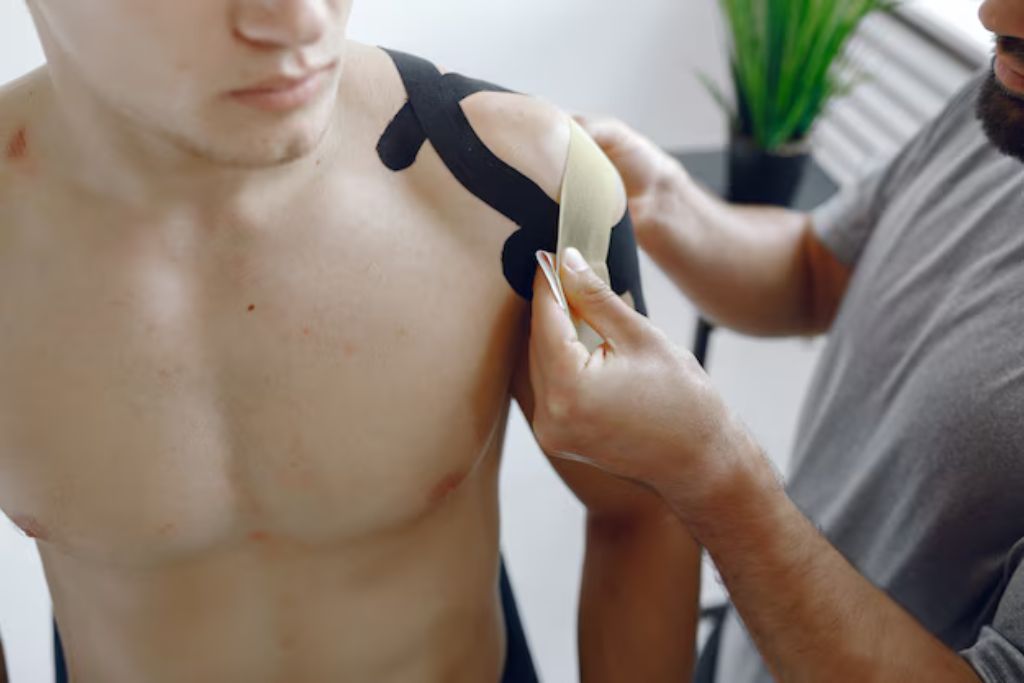
Taping
Taping eye therapy is a technique often used in the fields of physical therapy, rehabilitation, or aesthetics to help improve various conditions affecting the eye or surrounding areas. It can involve the use of adhesive tapes, such as kinesiology tape or specialized medical tapes, applied around the eyes or on the face to promote healing, reduce swelling, and support muscle function.
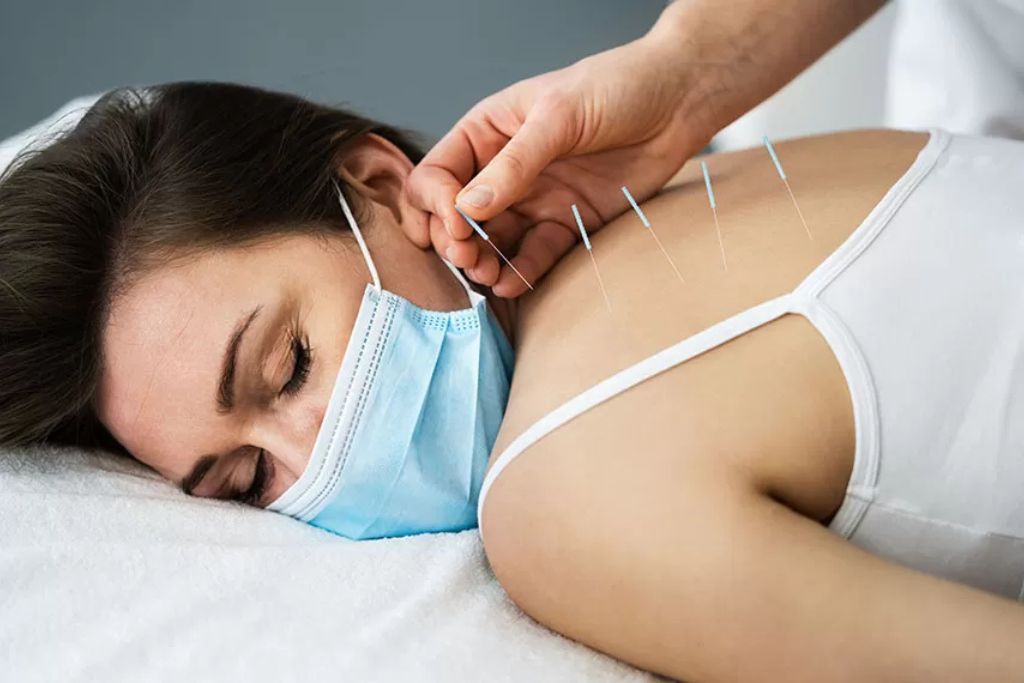
Dry Needling
Dry needling is a technique used by physical therapists and other trained healthcare professionals to treat muscle pain and tightness. The method involves inserting thin, filiform needles (similar to acupuncture needles) into specific points within the muscle, often referred to as trigger points. Trigger points are taut bands of muscle that can be tender and may cause pain, stiffness, or reduced function.
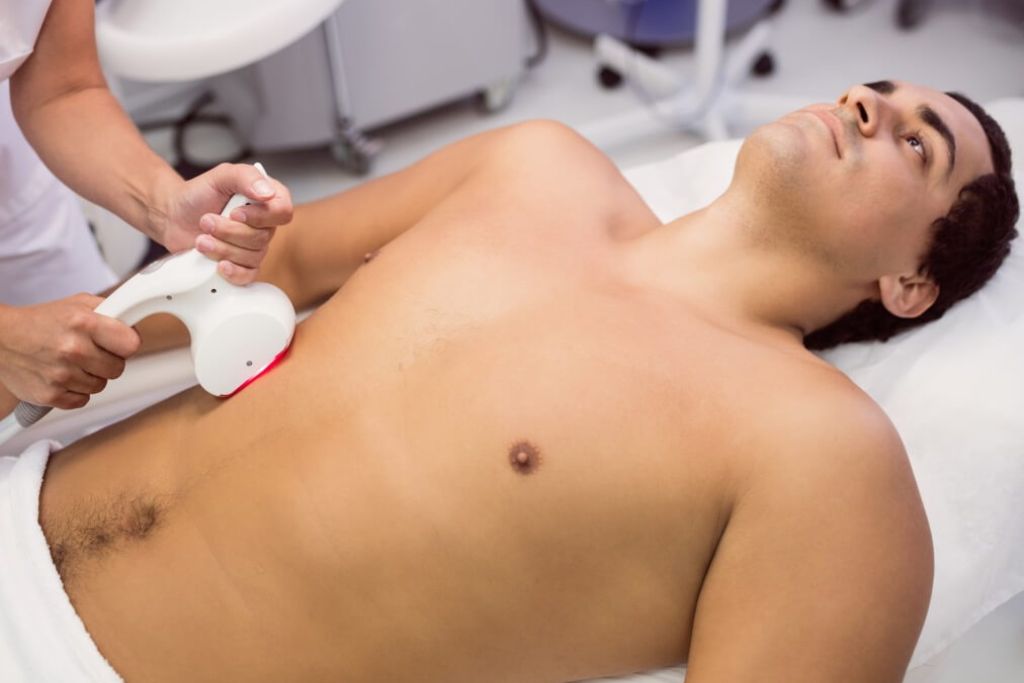
Laser
Laser eye surgery, commonly referred to as laser vision correction or refractive surgery, is a medical procedure that uses lasers to correct common vision problems such as nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), and astigmatism. The goal is to reshape the cornea (the clear front part of the eye) to improve how the eye focuses light onto the retina, leading to clearer vision and often reducing or eliminating the need for glasses or contact lenses.
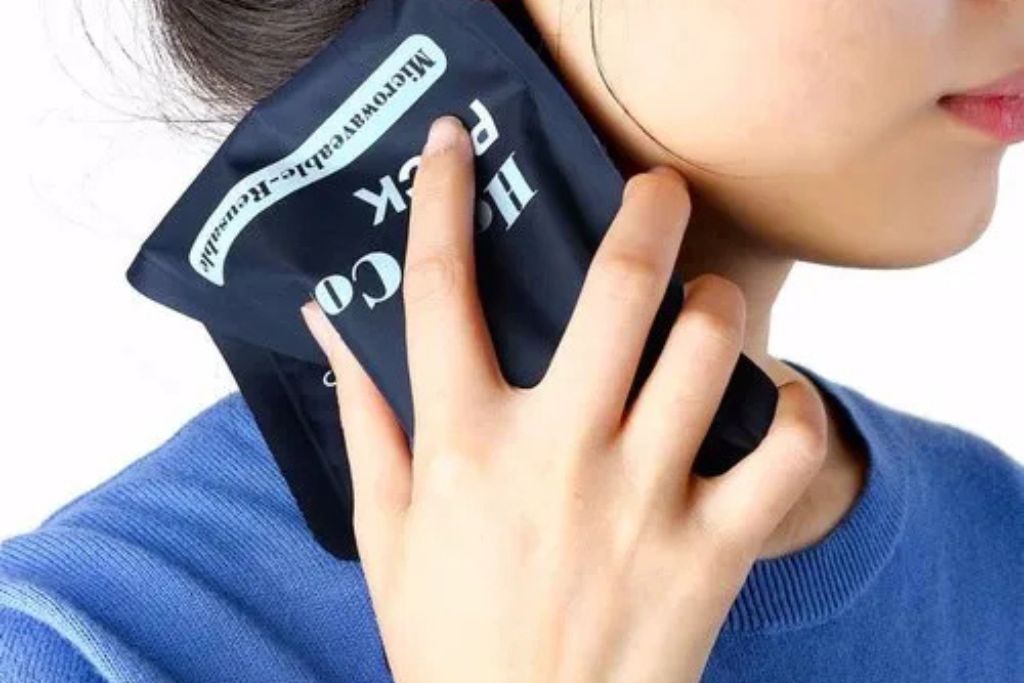

Hot/Cold
Hot and cold eye therapy is a simple and effective way to relieve various eye discomforts. Hot therapy involves applying a warm compress to the eyes, which helps improve circulation, relieve dry eyes, reduce styes, and soothe eye strain or sinus pressure. It’s especially helpful for conditions like meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) that affect the eye's natural oil production.
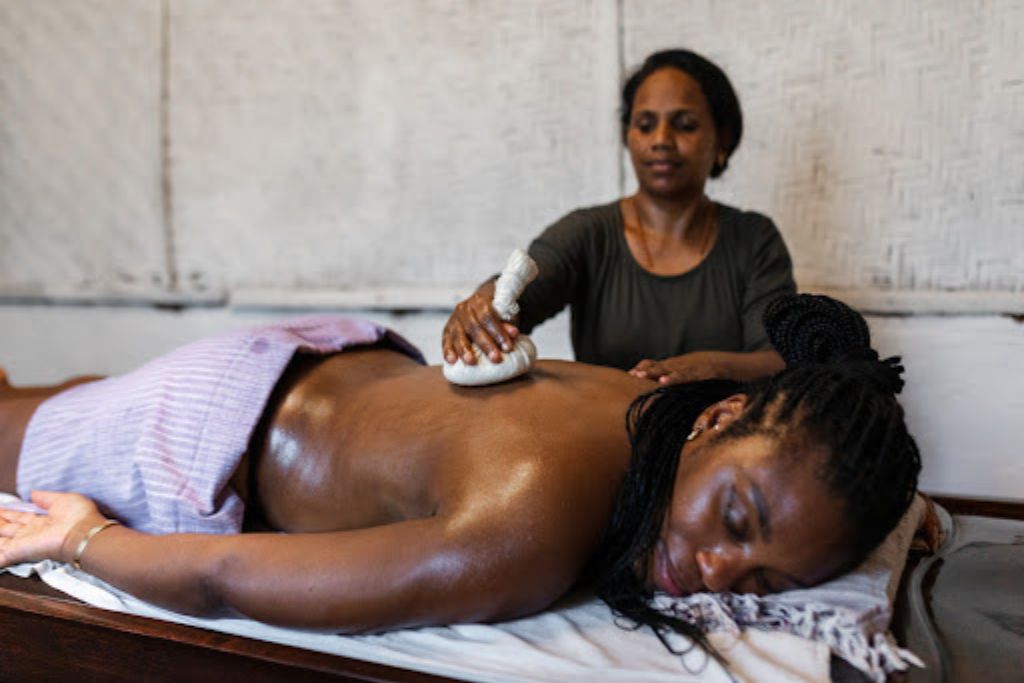

Fomentation
Fomentation is a therapeutic technique that involves applying moist or wet heat to a specific area of the body to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and relax muscles. It is commonly used in physical therapy to treat conditions like muscle strains, arthritis, and joint pain. The heat helps improve blood circulation by dilating blood vessels, which promotes healing and eases discomfort.
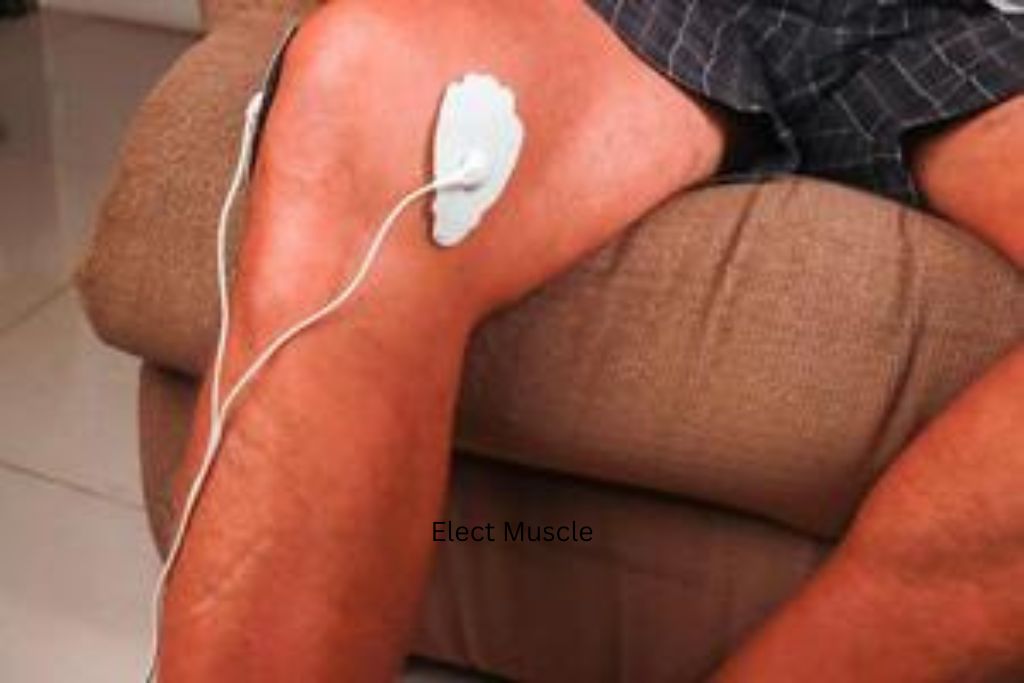
Elect Muscle
Electromyostimulation (EMS), also known as electrical muscle stimulation, is a technique that uses electrical impulses to cause muscle contractions. This method is often used in physical therapy, rehabilitation, and fitness training. EMS devices send low-level electrical currents through electrodes placed on the skin, which stimulate the motor neurons and cause muscles to contract, mimicking natural movements.

